Patient Identification Error, a Prevalent type Medical Malpractice
 Patient identification error may be medical malpractice that can result in serious injury and sometimes death of a patient. This type of medical error can happen at any step of a medical process from lab testing to medication administration and even billing.
Patient identification error may be medical malpractice that can result in serious injury and sometimes death of a patient. This type of medical error can happen at any step of a medical process from lab testing to medication administration and even billing.
A special report published by the ECRI Institute reviewed 160 recent scientific searches and publications written on this type of medical malpractice to provide a snapshot of the status of this prevalent occurrence.
The report found patient identification errors at each of the following clinical contexts:
- Registration
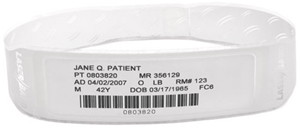
The report found that requiring a photo ID at registration and proceeding to a face-to-face confirmation of identity significantly reduces the risk of patient error at registration. - Wristband accuracy and use
Missing wristbands or wristbands containing information that is not accurate are an important factor of wrong-patient error. The design of the wristband also can lead to patient identification error. Wristbands too large for children, hand written wristbands that are difficult to read, bad quality ink that degrade with liquid exposure can all contribute to errors in identifying the patient. - Order entry and charting
Distraction and fatigue as well as having more than one chart opened at the same time have been identified in the ECRI report as the two main factors leading to errors in order entry and charting. - Medication administration
Due primarily to poor adherence to patient protocol by the nurse administering the medication, medication errors is unfortunately extremely common in the inpatient setting. Sometimes too complicated and inconvenient protocols can also be a factor in medication errors. Additionally bar-code glitches have also been identified as a potential cause of medication errors. - Radiology and surgery
Wrong site and wrong patient surgeries can cause significant harm to a patient. Over a 6 year period, the ECRI researchers found 25 cases of wrong patient surgeries. Five of them suffered serious personal injury and functional impairment. The surgery errors most of the time occurred because of patient identification errors during the diagnostic process, such as mixing up laboratory samples or medical records. A formal read-back by the surgical team could have averted most of these errors. - Laboratory, transfusion and pathology
The majority of patient identification errors during laboratory, transfusion and surgical-specimen processing are caused by mislabeling of specimens. The rate of error is especially high when the labeling and collection of the specimen is performed by non-laboratory personnel.
Based on the above report the ECRI Institute created a toolkit to help health IT to reduce patient identification error. The ECRI also published a list of recommendations to help healthcare providers make sure their patients are proprely identified.
Picture source: Wikipedia
 New York Personal Injury Attorneys Blog
New York Personal Injury Attorneys Blog


