Motorcycle Accident: Crashing without a Helmet significantly increases Risk of Head and Neck Injuries
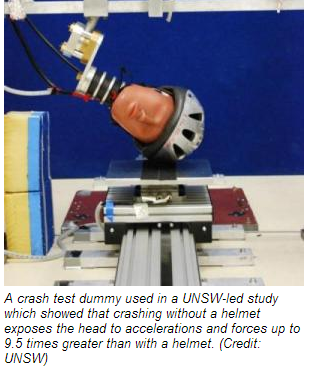 Motorcyclists who don’t wear a helmet have a much higher risk to suffer concussion or other serious skull or brain injury in a crash. A crash-test dummy shows that crashing without a helmet exposes the head to accelerations and forces up to 9.5 times stronger than with a helmet according to a recent study from the University of New South Wales and published in the Journal Traffic Injury Prevention
Motorcyclists who don’t wear a helmet have a much higher risk to suffer concussion or other serious skull or brain injury in a crash. A crash-test dummy shows that crashing without a helmet exposes the head to accelerations and forces up to 9.5 times stronger than with a helmet according to a recent study from the University of New South Wales and published in the Journal Traffic Injury Prevention
The test replicated the oblique impact on the head and on the neck after falling from a bike at different speeds and heights and compared the results of the impact on a helmeted and an unhelmeted head.
The results showed that a good helmet with tightly adjusted restraints can protect motorcyclists head from serious injuries even during the most severe impacts.
 New York Personal Injury Attorneys Blog
New York Personal Injury Attorneys Blog


 A research team led by Boris Rubinsky, Professor of the Graduate School at
A research team led by Boris Rubinsky, Professor of the Graduate School at 
 On the evening of July 24, 2001 Michael Taratuta, was walking on the sidewalk abutting a building when, suddenly, and without warning, a section of a security fence which was erected on the parapet wall surrounding the roof of the five-story brick, non-elevator building rising to a main roof elevation of approximately 59 feet fell to the sidewalk below, striking and seriously injuring Michael. As a result of the occurrence, Michael sustained grave injuries, including a traumatic
On the evening of July 24, 2001 Michael Taratuta, was walking on the sidewalk abutting a building when, suddenly, and without warning, a section of a security fence which was erected on the parapet wall surrounding the roof of the five-story brick, non-elevator building rising to a main roof elevation of approximately 59 feet fell to the sidewalk below, striking and seriously injuring Michael. As a result of the occurrence, Michael sustained grave injuries, including a traumatic 