A man who lost his leg after being treated for a broken ankle was awarded 9.1 million by a Jury in a New York Medical Malpractice Lawsuit
In a recent malpractice lawsuit, a New York State Supreme Court Jury, Erie County, awarded $6 million for past and future pain and suffering and $2.8 million for medical expenses and lost of wages to a man who lost his leg as the result of medical malpractice by his surgeon. His ex-wife was also awarded $350,000 for loss of services.
Donald Schultz was a 35 year old public safety dispatcher for the City of Tonawanda, NY, when he broke his ankle in 2004. After initial treatment he still felt pain on the side of his foot near the little toe and made an appointment with Dr. Michael A. Parentis at the Knee Center of WNY. Dr Parentis performed 12 surgeries on his foot and leg. He started with surgeries on the little toe then amputated it. After the patient developed an infection, the doctor also amputated the fourth toe. As the pain continued the doctor continued to operate up until July 2009 when he amputated the leg below the knee.
Read more in Buffalo news
 New York Personal Injury Attorneys Blog
New York Personal Injury Attorneys Blog


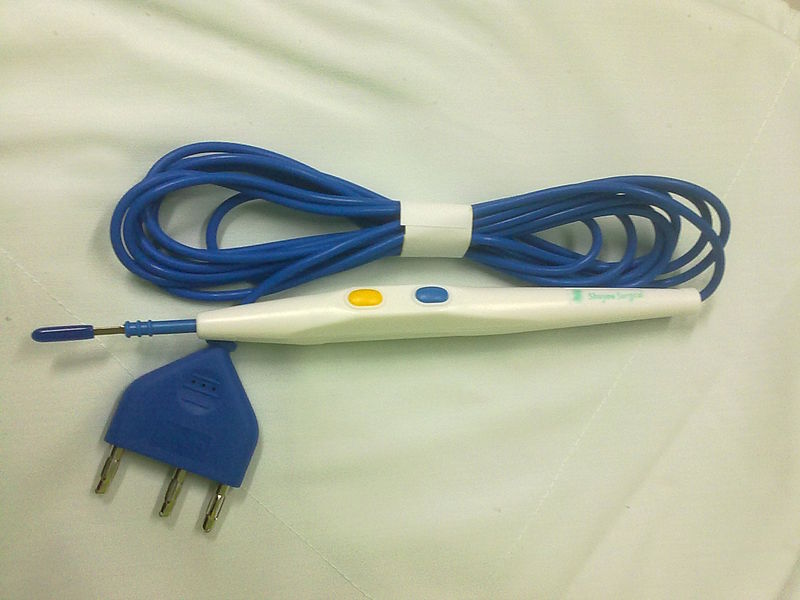 A recent study analysed all Medical Malpractice claims related to fires in the Operating Room that have been filed in the American Society of Anesthesiologists Closed Claims Database since 1985 and found that electrocauterization was responsible for 90% of the claims. The study “
A recent study analysed all Medical Malpractice claims related to fires in the Operating Room that have been filed in the American Society of Anesthesiologists Closed Claims Database since 1985 and found that electrocauterization was responsible for 90% of the claims. The study “
 A settlement in the amount of $1,750,000 was obtained by our partners New York Medical Malpractice Attorneys
A settlement in the amount of $1,750,000 was obtained by our partners New York Medical Malpractice Attorneys  Our Partner New York Medical Malpractice Attorney
Our Partner New York Medical Malpractice Attorney 
