90% of Medical Malpractice Claims related to Operating Rooms Fires are Claims of Burn Injury sustained during electrocauteization induced fires
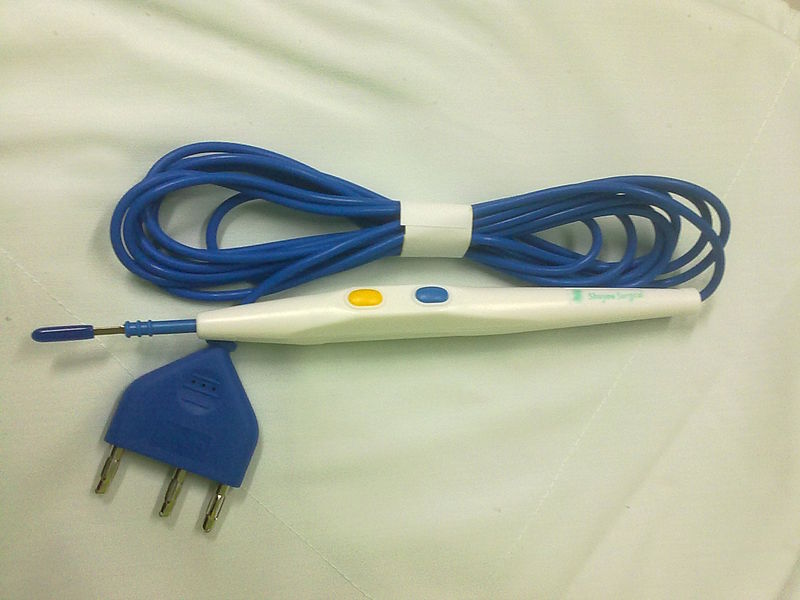 A recent study analysed all Medical Malpractice claims related to fires in the Operating Room that have been filed in the American Society of Anesthesiologists Closed Claims Database since 1985 and found that electrocauterization was responsible for 90% of the claims. The study “Operating Room Fires: A Closed Claims Analysis” was published in the Journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists” and led by Dr. Karen Domino, Professor & Vice Chair for Clinical Research Anesthesiology & Pain Medicine, Adjunct Professor, Neurological Surgery, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington.
A recent study analysed all Medical Malpractice claims related to fires in the Operating Room that have been filed in the American Society of Anesthesiologists Closed Claims Database since 1985 and found that electrocauterization was responsible for 90% of the claims. The study “Operating Room Fires: A Closed Claims Analysis” was published in the Journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists” and led by Dr. Karen Domino, Professor & Vice Chair for Clinical Research Anesthesiology & Pain Medicine, Adjunct Professor, Neurological Surgery, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington.
Electrocauterization or Electrocautery is a procedure that is used in surgery to burn unwanted or harmful tissues or to seal blood vessels to stop bleeding. During the procedure a surgeon uses heat conduction from a metal probe heated by electric current to burn the tissue.
The study found that most Electrocautery induced fires happen during monitored anesthesia care with open oxygen delivery for upper chest, neck and head procedures with plastic surgery procedures on the face accounting for more than half of them.
The percentage of cauterization fire claims have increased exponentially over time. Between 1985 and 1989 they were representing less than one percent of all surgical claims. According to the study they are now accounting for more than 10% of all surgical claims.

 New York Personal Injury Attorneys Blog
New York Personal Injury Attorneys Blog


